We are assuming you have C compiler already Installed in your systems, if not you can read How to install C compilers ? (Ubuntu, Mac, Windows)
What is C ?
C is high-level compared to assembly but low leveled compared to JavaScript. But in general terms C is considered as high level language.
So when we talk about c language, we usually hear the following terms
- Header file
- Data types
- Variables
- Main function
- Operators
- Hello World Program ( gateway to programming world 😉)
- Addition/Subtraction program for the basic understanding of Operators
- Header file
- Data types
- Variables
- Main function
- Operators
- Hello World Program ( gateway to programming world 😉)
- Addition/Subtraction program for the basic understanding of Operators
What is Header File ?
As a beginner I never got a satisfactory answer for the same. In a nutshell, we can say “It's just like a brain to a body”,
It enables us to use the functionality which is pre-implemented by the Developers, just like the brain adds the functionality to other body parts.
It enables us to use the functionality which is pre-implemented by the Developers, just like the brain adds the functionality to other body parts.
Header file has a file extension of '.h'
for example “stdio.h” also called standard input-output library which enables the functionality of input and Output Operations in the program.
Header File is declared at the top of the program in the following way
for example “stdio.h” also called standard input-output library which enables the functionality of input and Output Operations in the program.
Header File is declared at the top of the program in the following way
#include<headerfilename> #include<stdio.h>
Note: Header files allow us to use functions direclty in our program since they are already defined. Hence we can make up our own header file and use it.
Data Types in C
The term data refers to the piece of raw facts and figures. To categorise the data we use data types. In c there are four primitive data types.
Variables have some memory allocated with them and they allow us to store values in them.
How to declare variables?
dataType variableName;
For example:
int a; // This is Integer variable named as a.
char b; // This is Character variable named as b.
float c; // This is Float/decimal variable named as c.
How to Assign values to the Variables in C ?
We assign values using the assignment operator (=) which means copy the value from right to left
For example:
int a= 9;
char b="T";
float c=2.3;
How to print the output in C ?
The following function allows us to print the output on the computer screen
printf();
To print text you must wrap it in double codes
printf("some text");
To print integer values contained in a variable
printf(“%d”,i);
Where “%d” is a format specifier of the value that is being printed, interger in this case.
For float (decimal numbers), we use “%f”
For character, we use “%c”For String, we use "%s"
Main Function in C
The Main function is executed at very first place when we run the C program.
dataType main()
{
//code to be run
return 0;
}
Operators in C
Following are the arithematic operators used for doing operation between two or more operand
Example: addition of two numbers
 |
| Operators in C |
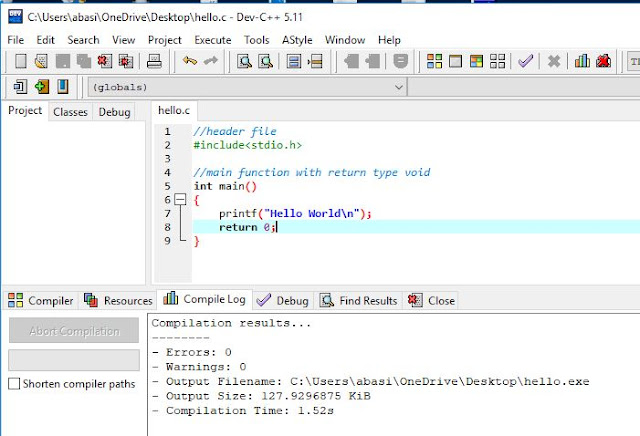
Hello World program in C
//header file
#include<stdio.h>
//main function with return type void
int main()
{
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}
printf() any text written between the double codes is printed as it is“hello world”
';' is used to denote the end of the statement(line of code).Addition/Subtarction program in C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h> //header file for doing maths(artithematic)
int main()
{
int a = 2;
int b = 3;
int sum = a+ b;
printf("sum of a + b is : %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
 |
| INPUT |
 |
| OUTPUT |
Till now you must have got an overview of the syntax and common terms used in C.
See you at part 2 where we will cover core topics: 101/Introduction to C language - part 2



Comments
Post a Comment